Life Science Outsourcing comprehensive medical package testing services include accelerated and real-time aging.
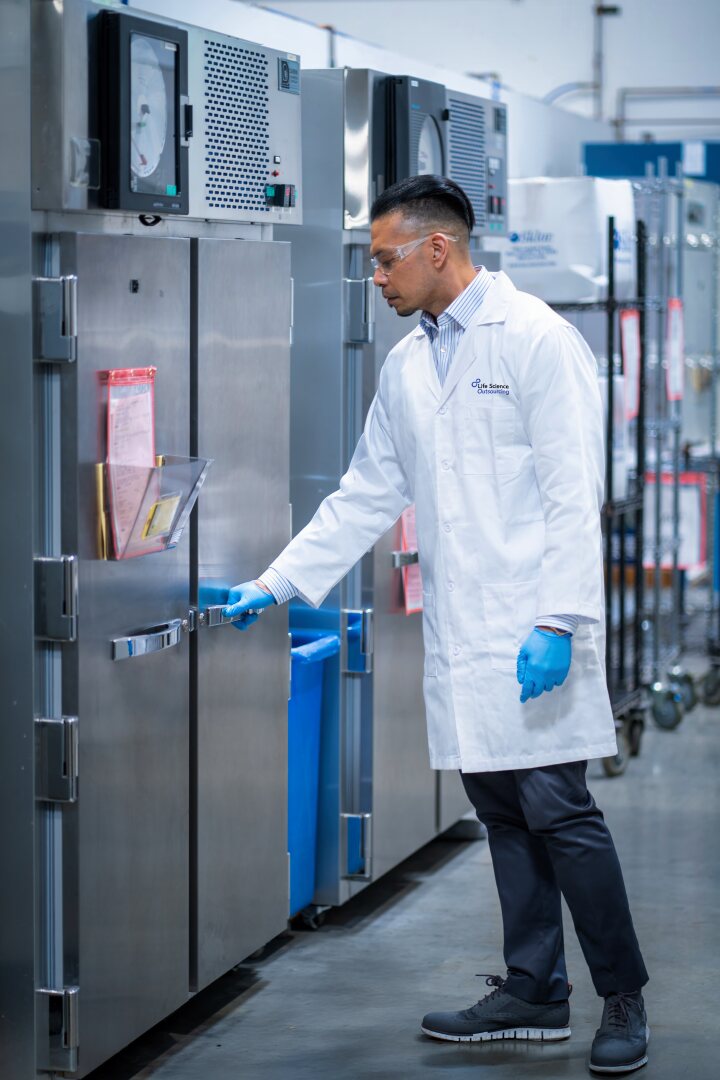

Ensure your medical device packaging meets regulatory standards and performs over time with LSO’s accelerated and real-time aging services. Accelerated aging speeds up the testing process, helping you get products to market faster, while real-time aging provides accurate data under expected conditions. With expertise in ASTM F1980 and ISO 11607 standards, we deliver dependable testing solutions, helping you validate performance, safeguard product integrity, and streamline compliance. Partner with LSO to confidently bring your devices to market.
Accelerated and real-time aging are methods to test how a medical device package will weather the impact of time, storage, and environmental exposure to heat, humidity, and more.
Real-time aging lets the package sit for a predetermined length of time and provides the most accurate assessment of packaging performance under expected conditions; accelerated aging testing places packaging in elevated temperature and humidity environments, allowing manufacturers to quickly obtain data that can be used for preliminary evaluations and expedite the testing process.

All manufacturers and stakeholders involved in production, distribution, and regulatory approval of medical devices need to use real-time aging data to ensure compliance and product safety; accelerated aging can help obtain a faster testing result to expedite product delivery to market.
Are you looking for guidance for your medical package age testing? This accelerated aging calculator generates a table of values for calculations based upon ASTM F1980, otherwise known as “Accelerated Aging of Sterile Medical Device Packages.”
This calculator generates a table of values for calculations based upon ASTM F1980, Accelerated Aging of Sterile Medical Device Packages.
Accelerated aging exposes packages to elevated temperature and humidity conditions to simulate aging effects over a shorter period and can predict how packaging will perform over its intended shelf life more quickly. It can be useful for speeding up the testing process and getting products to market faster.
Packaging
Medical devices are packaged in their final form.
Exposure
The packaged devices are subjected to elevated conditions of temperature and humidity that are higher than normal storage conditions.
Duration
Duration is often calculated to correspond to several years of real-time aging within a few weeks or months.
Testing
After the accelerated aging period, the packaging is tested for the same parameters as real-time aging (seal integrity, barrier properties, and more).
Real time aging stores packages under normal, expected conditions of temperature and humidity for the entire duration of their intended shelf life and observes how the package performs over time under realistic conditions.
Packaging
Medical devices are packaged as they would be for real-world use, including labeling and sealing processes.
Storage
The packaged devices are then stored under controlled conditions that replicate environmental conditions over the product’s shelf life.
Monitoring
The packaging is periodically inspected to assess physical integrity such as seal strength, barrier properties, and appearance. Intervals between inspections can be months or years, depending on expected shelf life.
Testing
Performance tests are conducted at regular intervals to determine if packaging continues to adequately protect the device.
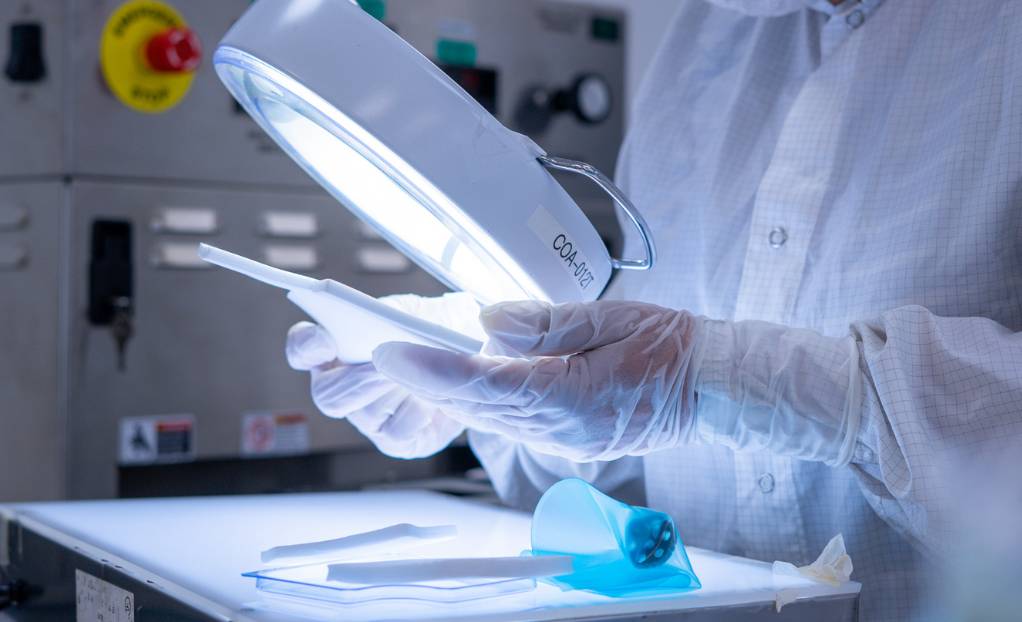


The FDA requires that packaging be tested to verify that it can maintain its integrity over intended shelf life. Real-time aging is often used to demonstrate this, although accelerated aging may also be employed. The FDA does allow the use of accelerated aging as a supplementary method to demonstrate package integrity, but usually needs to be supported by real-time aging data to meet regulatory requirements in full. ISO 11607 “Packaging for Terminally Sterilized Medical Devices” is used as the industry standard.”
Life Science Outsourcing has proven expertise and industry qualifications in medical device packaging design and validation. We work closely with your team to implement effective primary and secondary package design solutions and ASTM F1980 outsourcing to deliver your device to market faster.
Comprehensive packages for regulatory compliance.

From fractional to full cycles with EtO residual testing.
Secure with 2X qualification.
Tailored to your sterilization needs.
Life Science Outsourcing is an FDA registered and ISO 13485 certified full service Medical Device Contract Manufacturer.
We improve our products and advertising by using Microsoft Clarity to see how you use our website. By using our site, you agree that we and Microsoft can collect and use this data. Our privacy notice has more details.
Receive the latest infographics, guides, and blog updates for medical device manufacturing, package testing, and sterilization.