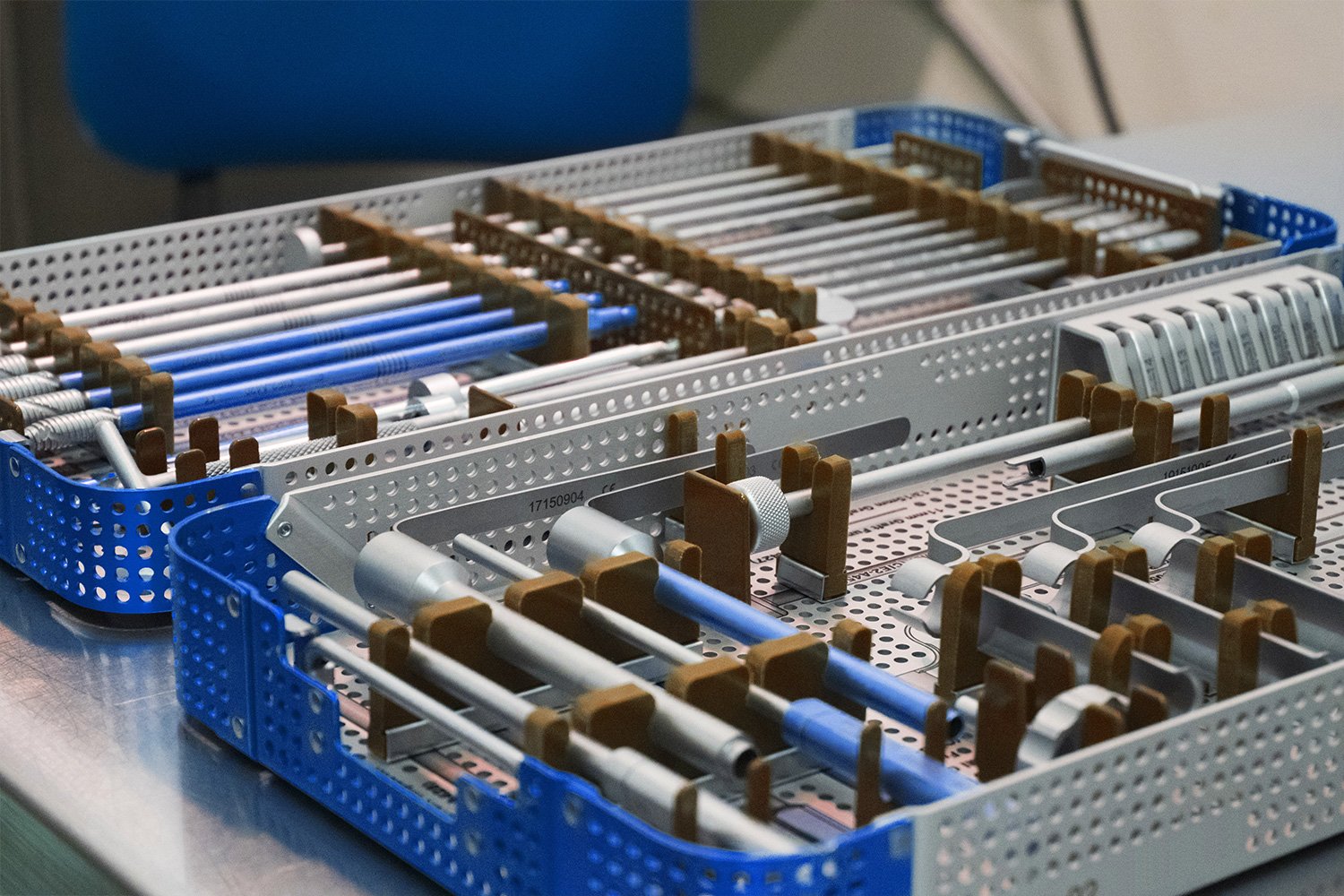
Medical devices must be sterilized and prepared before use. There are several best practice and integrity recommendations to consider when your devices require sterilization, including cleaning and packaging.
First, let’s look at why sterilization services are so critical and how they are achieved.
Medical device sterilization is performed to kill disease-causing microorganisms and eliminate transmissible agents. These agents can include spores and bacteria. Clearly this is necessary for patient safety and improved outcomes.
Sterilization is achieved through several methods, which can include:
- Wet/steam sterilization
- Dry heat sterilization
- Ethylene oxide
- Sporicidal chemicals
- Glass plasma
- Irradiation (gamma rays)
But what about those best practice recommendations? The following are 7 ways to improve sterilization outcomes:
Effective Cleaning
Effective cleaning is necessary to achieve sterilization. The issue here is bioburden, which can negatively impact the sterilization process. Cleaning the device prior to sterilization removes soils, oils, and other materials that might otherwise shield existing microorganisms from sterilant contact. A proper cleaning will remove such bioburden and allow for efficient sterilization.
The Right Packaging
The best packaging will be the most effective by following industry standards. It is important to follow medical device packaging industry standards which can ensure sterility, and in fact, maintain sterility until the device is used. Three types of packaging are most common for medical devices: flat wrappers, paper-plastic peel pouches, and sterilization containers.
Storage
Minimizing exposure to moisture, humidity, dust, and other potentially impactful environmental issues is a priority. Sterilized materials should be appropriately packaged, labeled, and properly stored in order to minimize such exposure. An additional important step is to verify each item with a marked sterilization date.
Transportation
Sterilized devices can be impacted not only by the storage conditions mentioned above, but also by transportation activity such as handling and external conditions. Transportation methods can also impact packaging quality.
Sterilization Records
Local, state, and federal regulations compliance must be observed for sterilization records, as must healthcare organization policies. Critical documentation pieces should include:
- Assigned lot number
- Contents of each load
- Results of physical, chemical, and biological monitors
Policies and Procedures
Policies and procedures for medical device sterilization should be developed, periodically reviewed, and easily accessed within the practice setting.
Quality Control Programs
Patient safety is paramount, as is employee safety. Proper protocols should be in place to ensure that safety. Effective quality control programs can deliver on that, as well as achieve two more important goals: Enhancing employee performance, and monitoring sterilization efficacy.
Working with a company to ensure all these points are covered is crucial to your own medical device business process.
Partners such as Life Science Outsourcing can help you follow regulatory compliance and best practices for a successful device sterilization validation.